What is File History in Windows 10?
File History is a built-in tool that was first introduced in Windows 8. It allows you to recover files you might have accidentally deleted or restore a modified document to an earlier version. It’s essentially like Apple’s Time Machine but for Windows. To use it, you’ll need an external hard drive or a large-capacity USB flash drive. You can set it up to use a network location, too. File History will automatically back up Favorites, Contacts, Desktop items, and more. All this data can add up in a hurry, but you can configure File History to exclude certain folders and how often it saves copies of files.
Turn On File History
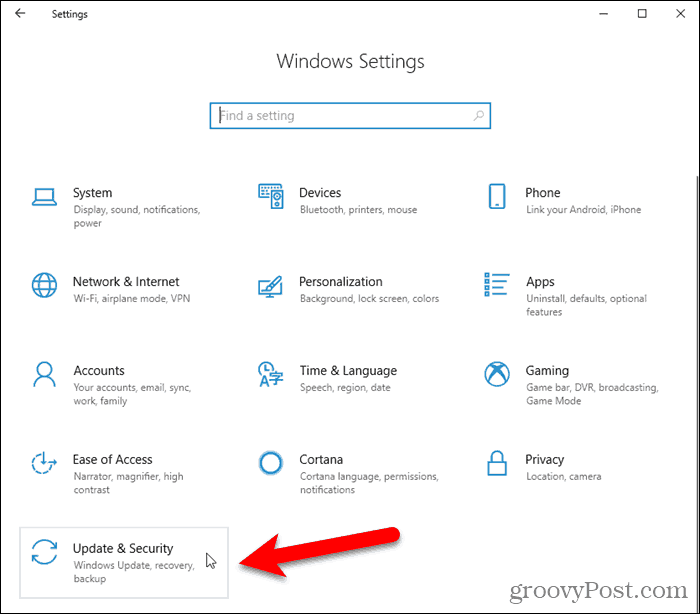
File History is turned off by default. To begin, connect your external drive. Then, open PC Settings from the Start menu and click Update & Security.
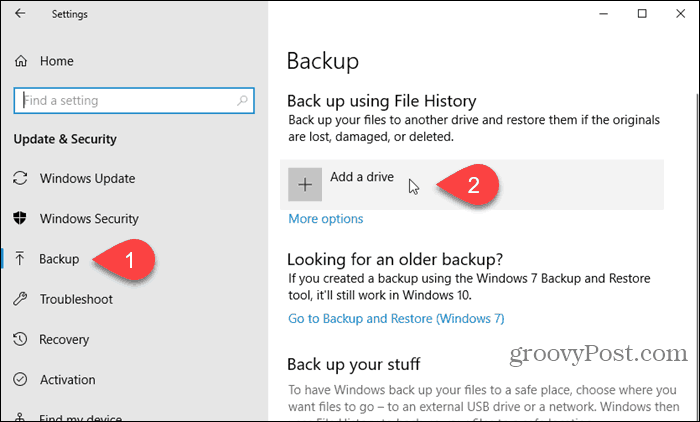
On the left pane, click Backup. Then, click Add a drive on the right.
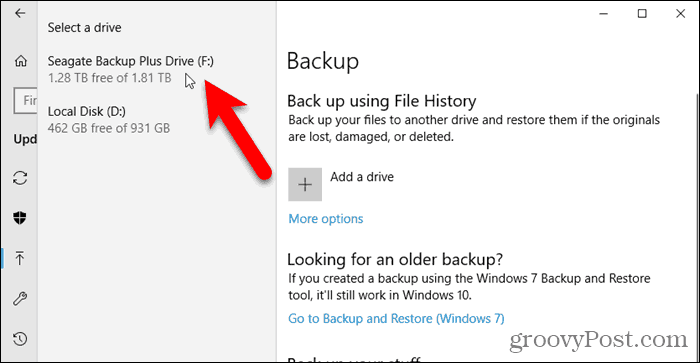
A list of available drives displays on the left. Click the one you want to use.
Configure File History
Once you select a drive, Windows automatically turns on File History. To configure File History, click More options on the Backup screen.
The Backup options screen allows you to set how often File History backs up your files and how long versions are saved. Select options from the Back up my files and Keep my backups drop-down lists.
File History automatically adds certain folders to the backup. So before you begin the backup process, you can remove folders you don’t want to back up. Under Back up these folders, select a folder you don’t want to back up and click Remove. Repeat for each folder you want to remove.
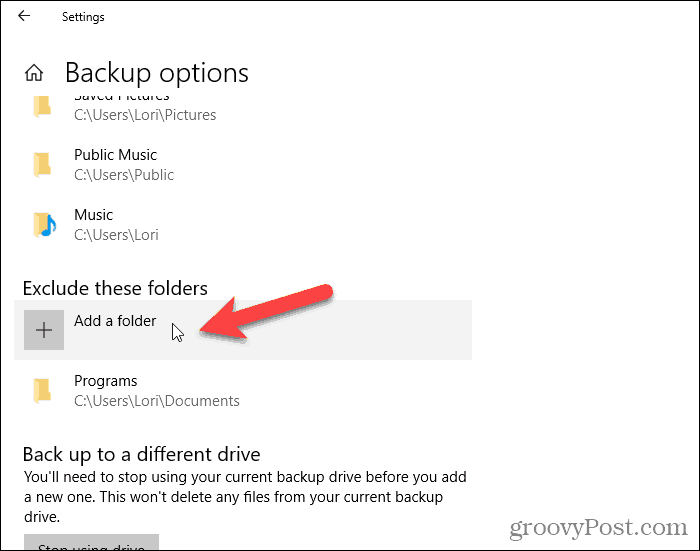
You can also specifically exclude folders. So, for example, if there’s a subfolder in one of the folders being backed up that you don’t want to back up, you can exclude that subfolder. Under Exclude these folders, click Add a folder. Next, select a folder to exclude on the Select Folder dialog box and click Choose this folder.
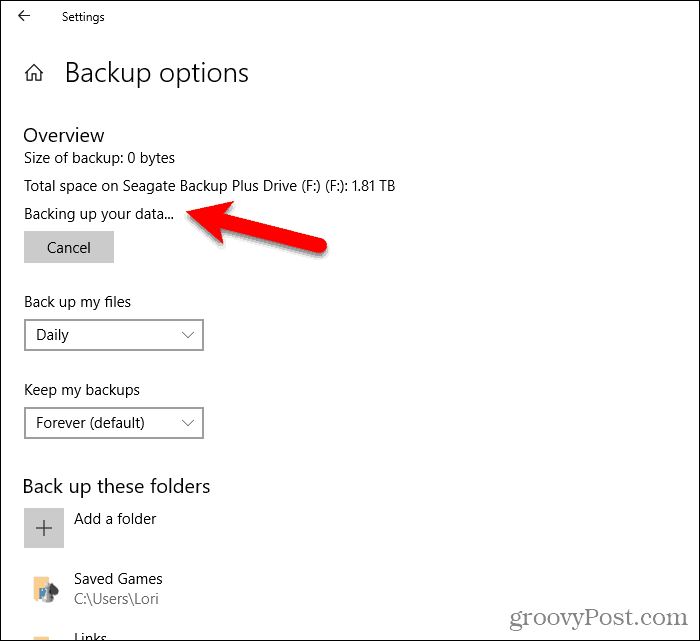
When you ready to start the backup process, click Back up now under Overview. You’ll see a message saying File History is backing up your data. But, unfortunately, there is no estimated time listed. So the initial backup may take a while.
Back-Up to a Network Location
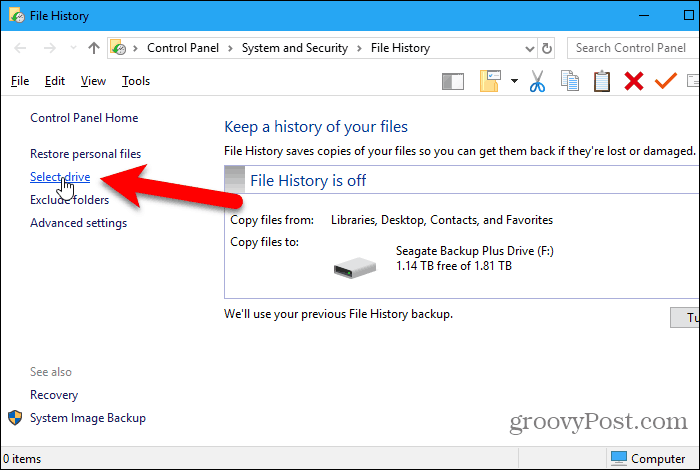
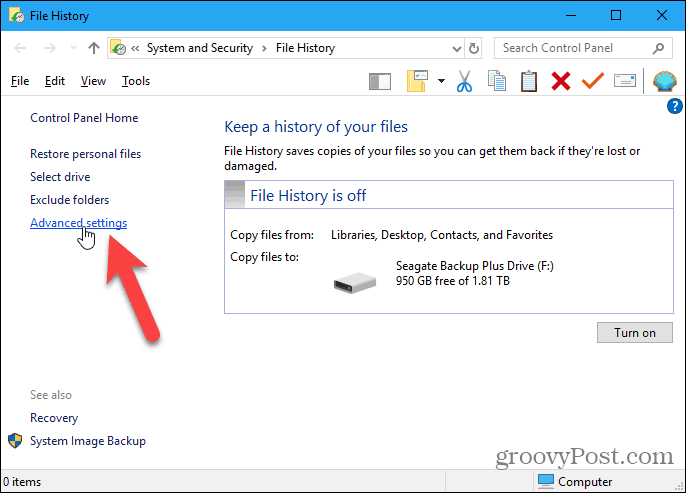
As we mentioned previously, you can use a network location for your backup as well. For example, maybe you have a home server or network-attached storage (NAS) box that you want to use. Go to the Backup options screen, if you’re not already on it, and click See advanced settings under Related settings.
Click Select drive in the right panel on the File History screen in the Control Panel.
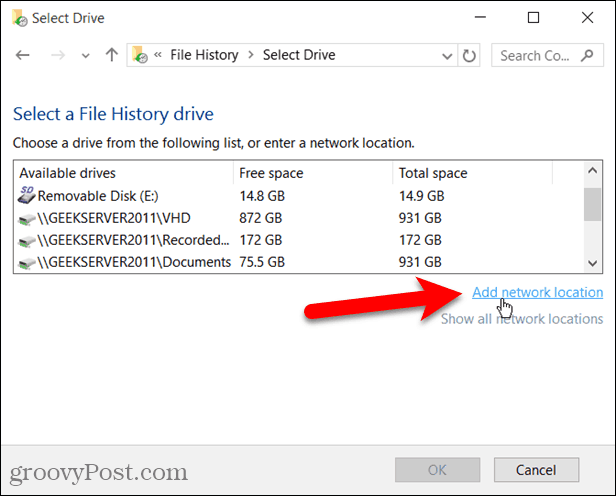
On the Select a File History drive screen, you’ll see local and network drives listed. If you don’t see the network drive, you want to use, click Add a network location and select it.
Recover Files Using PC Settings
Suppose you need to recover a file or directory stored on a local drive (not cloud storage), open PC Settings, and go to Update & Security > Backup. Then, click More options.
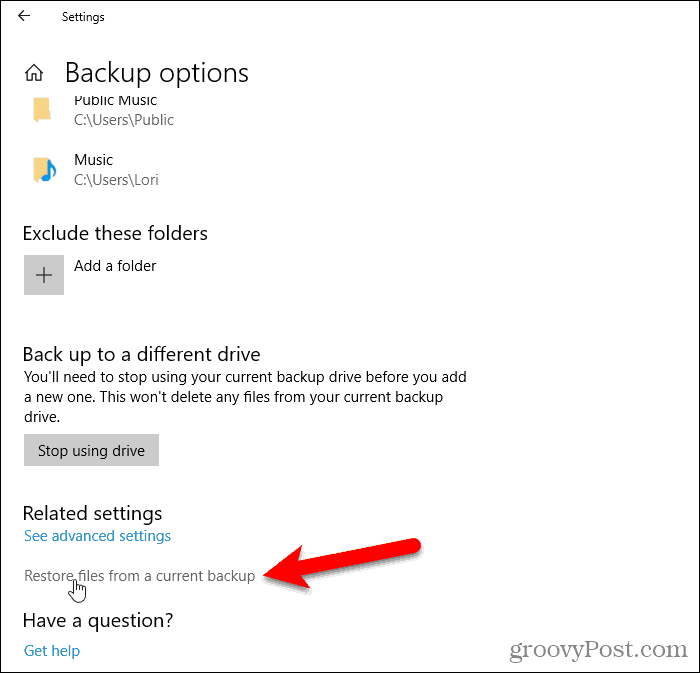
On the Backup options screen, click Restore files from a current backup under Related Settings.
Navigate to the file you want to restore and use the arrow buttons to select a version of the file to restore. Then, click the green Restore button.
Recover Files Using File Explorer
Or you can use File Explorer to restore a previous version of a file. Open up File Explorer and select the file you want to restore a version of. Then, click History on the Home tab.
Again, you can go back in time using the arrow buttons and select a different version of the files to restore. Click the green restore button to restore the selected version.
Or, you can right-click a file and select Properties. Then, click the Previous Versions tab and select the version of the file you need. This is a good way to grab an individual document you made changes to but want to work with a previous draft instead. Click Restore to restore the version of the file to the original location. If you want to restore the file to a different location, click the down arrow on the Restore button and select Restore To. On the Restore to dialog box, navigate to the folder where you want to restore the selected version of the file and click Select Folder. If the file already exists in that location, you’ll be asked if you want to replace the file.
Clean Up File History
After a while, depending on the drive size and your configured settings, you might get a notification that you need to free up space on your File History drive.
If you get that message, go to PC Settings > Update & Security > Backup > More options > See advanced settings. Then, click Advanced settings on the left.
On the Advanced settings screen, click Clean up versions.
Select how far back you want to delete folders and files from the drop-down list. Then, click Clean up.
Backing Up Should Be Part of a Regular Routine
Make sure you back up regularly to avoid data loss. File History backs up data files, but not the Windows system. But you can create a Windows 10 system image to do that. You can also create a Windows 10 restore point to go back in time to a previous version of your system. This is useful if you’re going to install some software and want a way to go back to before the installation if something goes wrong. Creating a system restore point is also recommended before making changes to the registry. Of course, the registry can be backed up on its own, too. If Windows 10 becomes slow and unresponsive at times, you can reset it. This resets Windows 10 to factory default but keeps all your data. After a reset, you must reinstall all your software, so be sure you have the time to do this before resetting Windows 10. Windows 10 is defaulting her WordPerfect documents into Word 2010. How do I help her set the default word processor? That makes a HUGE difference when you’re trying to restore an entire folder. In Time Machine, you grab the desired date and restore. ALL files, even those that haven’t changed in a month, will get restored. Which is what you want, since you are restoring an entire folder. With File History, you only get files that changed ON THAT DATE. Half or more of your restored folder could be missing. And there’s no way to know which files you are missing. It is absolutely worthless for anything other than restoring an individual file here and there. Comment Name * Email *
Δ Save my name and email and send me emails as new comments are made to this post.
![]()